SEO vs. SEM: WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SEO and SEM?
The world of digital marketing is filled with acronyms and jargon, which can be confusing for newcomers and veterans alike. One common question that arises is about the SEO and SEM differences. Knowing the difference between SEO and SEM can help you create a more effective digital marketing strategy.
In this article, we will discuss the key distinctions between SEO and SEM and highlight the importance of each in the digital marketing landscape.
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of improving your website’s visibility in organic search results. It involves optimizing various aspects of a website, such as content, meta tags, and technical factors, to rank higher in the search engine result pages (SERPs). The main goal of SEO is to increase organic traffic to your website.
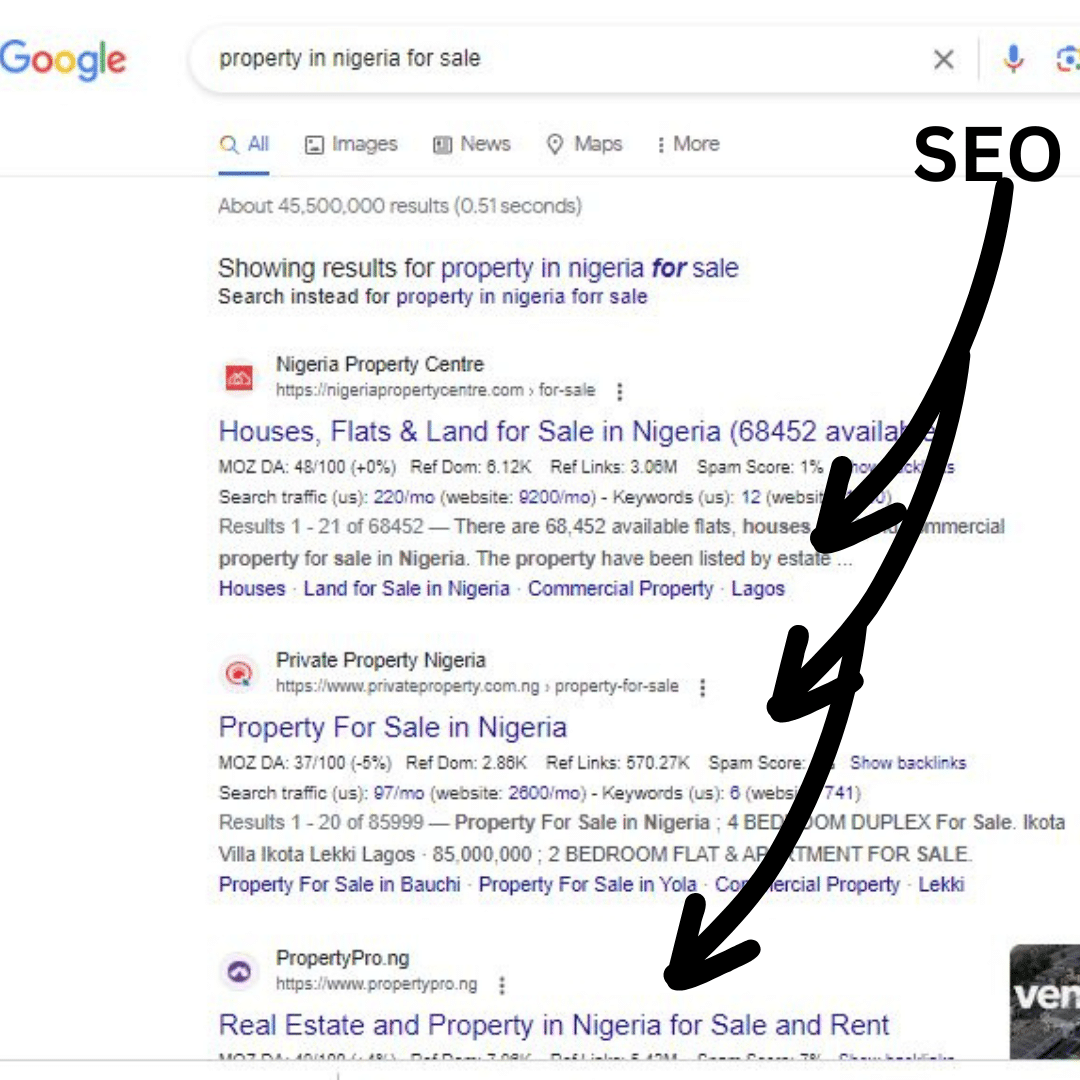
SEO can be broken down into three main categories: on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO.
1. On-page SEO
On-page SEO refers to the optimization of website elements that are visible to users and search engines. These include:
-
Keyword research and optimization
Identifying relevant keywords and phrases that users search for and strategically incorporating them into your website’s content, headings, and URLs.
-
Meta tags and title optimization
Creating descriptive and engaging meta titles and meta descriptions for each page, helps search engines understand the content and can improve click-through rates from SERPs.
-
Content quality and relevance
Publishing high-quality, unique, and informative content that provides value to users and answers their search queries.
-
Internal linking and site structure
Using internal links to connect related pages within your website, which helps users navigate and search engines crawl and index your content more efficiently.
2. Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO involves activities outside your website that can influence its ranking in SERPs. These include:
-
Backlinks and link building
Acquiring high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites, which act as “votes” for your website and signal its credibility and relevance to search engines.
-
Social media engagement
Promoting your content on social media platforms, which can increase brand exposure and drive more traffic to your website.
-
Guest blogging and content marketing
Writing guest posts for other websites or creating shareable content like infographics, can attract backlinks and improve your online reputation.
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the backend structure and foundation of a website to improve its performance and visibility in search engines. Key aspects include:
- Site speed and performance
Optimizing website load times and performance to provide a better user experience and improve search engine rankings.
- Mobile-friendliness and responsive design
Ensuring your website is accessible and easy to use on all devices, particularly mobile phones, as search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites.
- Structured data and schema markup
Adding structured data to your website’s HTML code, helps search engines better understand your content and can lead to enhanced search results, such as rich snippets or knowledge panels.
Pros and cons of SEO
Pros:
- Long-term, sustainable results
- Cost-effective compared to paid advertising
- Builds trust and credibility with users
- This can lead to a higher click-through rate from organic search results
Cons:
- Takes time to see significant results
- Requires ongoing effort and maintenance
- Algorithm updates can impact rankings
- Competitive keywords may be difficult to rank for
ALSO READ: Importance of Keyword Research In SEO
What is SEM?
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a broader term that encompasses all activities aimed at increasing a website’s visibility in the search results, including SEO and paid search advertising. Paid search, also known as pay-per-click (PPC), involves bidding on keywords to appear at the top of the search results.
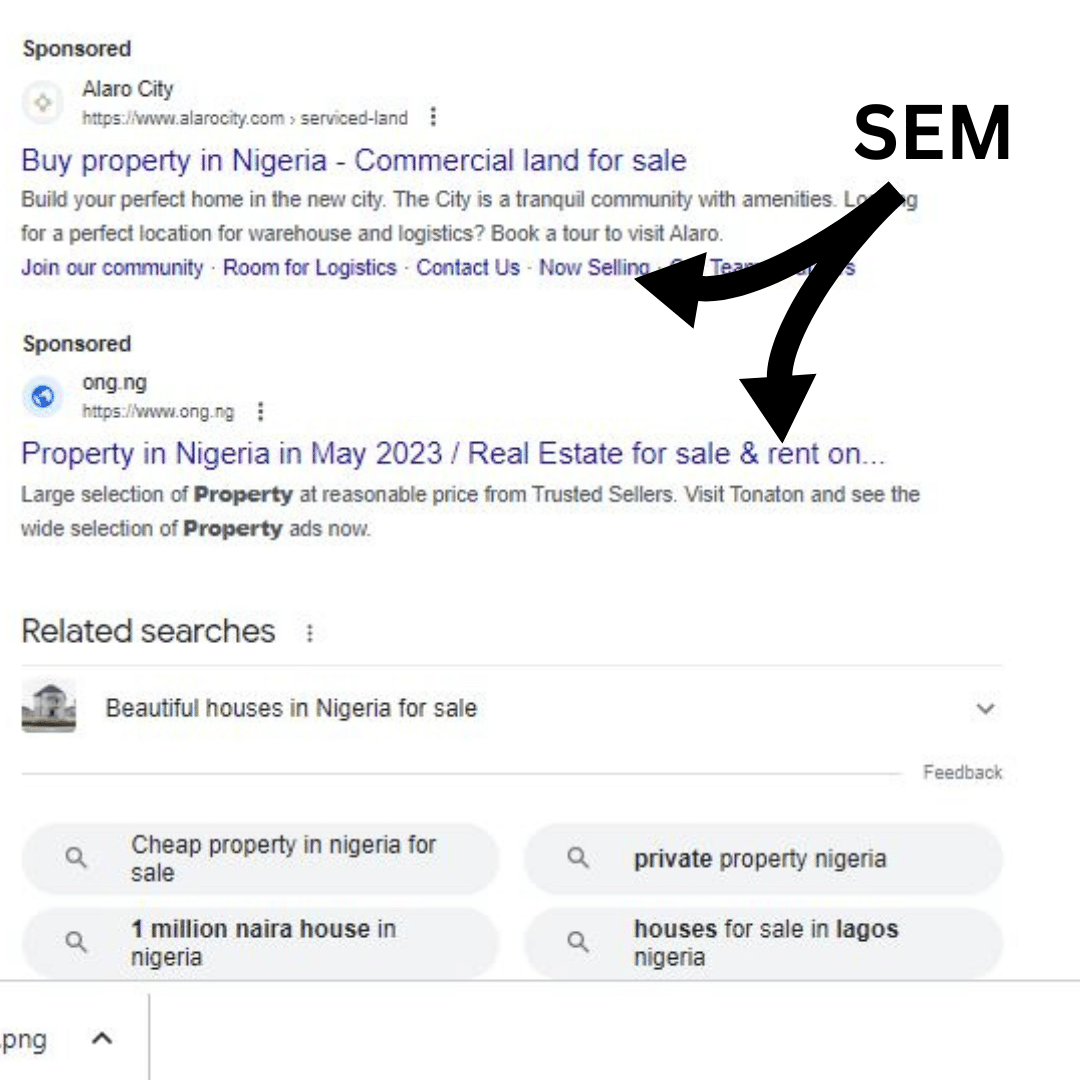
SEM helps businesses achieve immediate visibility in the search results and drive traffic to their websites through both organic and paid channels.
B. Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising
PPC is a type of online advertising where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. The most popular PPC platforms are:
-
Search ads
Also known as paid search or pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, are online advertisements that appear alongside organic search results on search engine results pages (SERPs) like Google, Bing, or Yahoo.
Advertisers bid on specific keywords related to their products or services, and when users search for those keywords, the ads may appear above or below the organic search results depending on the ad’s quality score and bid amount.
Some key components of search ads include:
- Ad copy: The text and headlines that make up the content of the ad.
- Keywords: The terms that advertisers target to trigger their ads to show up in search results.
- Landing page: The webpage that users are taken to when they click on an ad.
- Quality score: A metric used by search engines to determine the relevance and quality of an ad based on factors like click-through rate (CTR), ad relevance, and landing page experience.
- Bid amount: The maximum amount an advertiser is willing to pay each time a user clicks on their ad.
To create and manage search ads, advertisers typically use platforms like Google Ads or Microsoft Advertising. These platforms provide tools for keyword research, bidding strategies, ad creation, and performance tracking.
Effective search ads require ongoing optimization, including fine-tuning keywords, adjusting bids, and testing different ad copy and landing pages to improve performance and achieve a better return on investment (ROI).
Pros and cons of SEM
Pros:
- Immediate visibility: SEM allows businesses to gain instant visibility on search engines and social media platforms.
- Targeted audience: Advertisers can target specific demographics, interests, and behaviors, ensuring their ads reach the right audience.
- Measurable results: SEM offers detailed analytics, allowing advertisers to measure the success of their campaigns and optimize as needed.
Cons:
- Cost: Depending on the competition and industry, SEM can be expensive, especially for small businesses with limited budgets.
- Complexity: Managing SEM campaigns requires expertise in various platforms and tools, as well as an understanding of best practices and trends.
The Difference Between SEO and SEM
While there is some overlap between SEO and SEM, the main difference between SEO and SEM is that SEO focuses on improving a website’s visibility in the organic search results, while SEM encompasses both organic and paid search strategies.
Some key differences between SEO and SEM include:
-
Cost
SEO is generally considered a more cost-effective strategy, as it focuses on increasing organic traffic without the need for paid advertising. On the other hand, SEM involves paid search campaigns, which can be more expensive but provide faster results.
-
Timeframe
SEO is a long-term strategy that requires ongoing effort and can take months to see significant results. SEM, particularly PPC campaigns, can produce immediate results but may require a higher budget.
-
Visibility
SEO aims to improve a website’s visibility in organic search results, while SEM encompasses both organic and paid search strategies. This means that SEM can provide greater overall visibility in the search results.
-
Targeting
Both SEO and SEM allow for precise targeting of keywords and audiences. However, SEM offers additional targeting options, such as location, device, and demographic targeting, through its paid search campaigns.
-
Competition
SEO can be highly competitive, as businesses vie for the top organic search positions. SEM, on the other hand, allows businesses to bid on keywords and secure prominent ad placements, making it easier to compete with other businesses in their industry.
ALSO READ: How To Boost Your Business With Google Search Ads
Which Strategy is Right for Your Business?
The choice between SEO and SEM depends on your business goals, budget, and timeline. If you want to build long-term, sustainable traffic from organic search results, SEO is the way to go.
However, if you need immediate visibility and are willing to invest in paid advertising, SEM might be a better option. Below are some of the factors you might need to consider;
1. Assessing your goals and objectives
Before deciding on a marketing strategy, it’s essential to identify your business goals and objectives. These can include increasing brand awareness, generating leads, driving sales, or improving customer engagement. By clearly defining your goals, you can choose the most appropriate tactics and measure the effectiveness of your efforts.
2. Analyzing your target audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial for developing a successful marketing strategy. Research your ideal customers‘ demographics, interests, behaviors, and pain points to create relevant and engaging marketing campaigns. This information can also help you determine which platforms and channels are most effective for reaching your target audience.
3. Evaluating your budget and resources
Consider your available budget and resources when choosing a marketing strategy. If you have a limited budget, focusing on organic tactics like SEO may provide better long-term results.
However, if you’re looking to achieve immediate visibility and have the resources to invest, SEM may be more suitable. It’s essential to find a balance between your budget, resources, and expected outcomes.
4. Determining the best mix of SEO and SEM tactics
A successful digital marketing strategy often combines both SEO and SEM tactics. While SEO focuses on improving organic search rankings, SEM involves paid advertising to increase visibility.
Determine the best mix for your business based on your goals, target audience, and budget. For example, if your goal is to generate leads in a competitive market, you might consider using PPC advertising while also implementing SEO strategies to improve your website’s organic rankings over time.
5. Monitoring and adjusting your strategy for optimal results
Continuously monitor your marketing efforts to measure their effectiveness and make data-driven decisions. Use analytics tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI). Regularly review and adjust your strategy based on these insights to optimize your results and achieve your business goals.
In many cases, businesses can benefit from a combination of SEO and SEM strategies. By focusing on both organic and paid search, you can maximize your website’s visibility in the search results and drive more traffic to your site.
Encouragement to continuously learn and adapt in the ever-changing world of digital marketing
The landscape of digital marketing is constantly evolving, with new technologies, trends, and best practices emerging regularly. To stay ahead of the competition, marketers must continually educate themselves and adapt their strategies to keep up with these changes.
By embracing a growth mindset and staying informed on the latest developments in SEO and SEM, businesses can ensure they’re making the most of their digital marketing efforts and maintaining a strong online presence in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
In conclusion
Understanding the SEO and SEM difference is crucial for developing an effective digital marketing strategy. By leveraging the strengths of both approaches and adapting them to your specific needs, you can significantly improve your online presence and achieve your business goals.
A successful digital marketing strategy requires a well-rounded approach that integrates both SEO and SEM tactics. By combining these two methods, businesses can maximize their online presence, attract more potential customers, and ultimately boost their bottom line.
It’s crucial to understand the unique strengths and limitations of each tactic, as well as how they can work together to achieve a company’s marketing goals.